BASED ON LATEST GENERATION GALVANIC SYSTEM
The plant is designed for treating the wastewater resulting from the galvanic processes and relevant preparation and washing operations
- Treatment of the galvanic wastewater resulting from the intaglio plate making department (G)
- Pre-treatment of wastewater containing solvents, resulting from the offset plate making department (S)
- Treatment of PolyWash wastewater (P)

- Copper deposition
- Nickel deposition
- Chromium deposition
- Electrolytic dechroming
- Electrolytic degreasing
- Chemical degreasing
- Plate polishing
- Offset plate making
- Polymeric plate making
The plant capacity* is:
- 1400 l/day for the galvanic effluent
- 700 l/day for the offset plate making effluent
- 700 l/day for the PolyWash wastewater
*The capacity can be adapted to the customer’s requirement.
-
- Collection of wastewaters containing solvents
- Collection of galvanic wastewater containing chromium
- Collection of galvanic wastewater containing copper and nickel
- Collection of PolyWash wastewater
- Physical-chemical treatment
- Filtration and neutralisation
- Electric control cabinet
- Very compact and dehydrated solid waste
- Very reduced energy consumption.
- CE conformity in compliance with 2006/42/CE
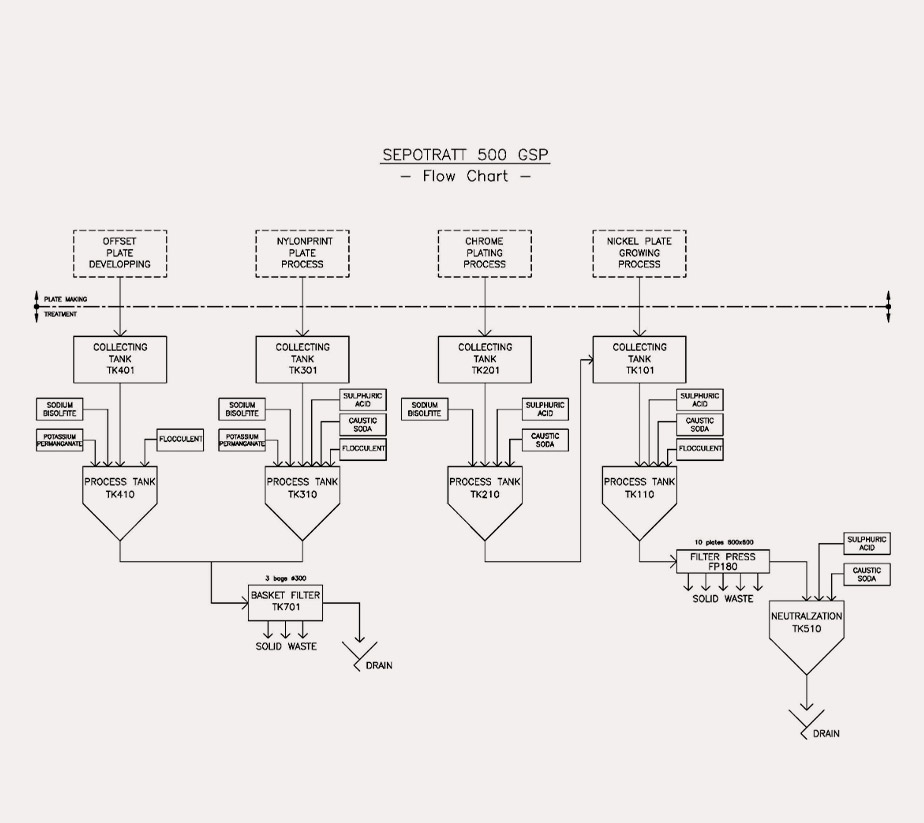
Wastewater containing solvents
The wastewater containing solvents, coming from the offset plate making department, is preliminary stored in a collecting tank and then transferred to the pre-treatment tank. The process, carried out by batch, consists of the subsequent addition of the following chemicals:
- Potassium permanganate (KMnO4), for solvents oxidation
- Sodium bisulphite (NaHSO3), to start flocculation
- Flocculent, to complete flocculation
Once accomplished the process, the basket filter enables the separation of the flocculated matter from the effluent, which is then transferred to the collecting tank containing copper and nickel effluents.
Wastewater containing chromium
The wastewater containing chromium is collected in a specific storage tank, separately from the rest of the galvanic wastewater, and then transferred to the process tank for chromium reduction. Particularly, the treatment consists of the subsequent addition of chemicals:
- Sulphuric acid (H2SO4), to decrease the pH value of the solution
- Sodium bisulphite (NaHSO3), to reduce chromium from hexavalent to trivalent
Once this pre-treatment carried out, this effluent is transferred in the collecting tank of the other galvanic water.
Wastewater containing copper and nickel
The wastewater containing copper and nickel is stored in a collecting tank, where also the other pre-treated waters are conveyed. The resulting effluent is transferred into the process tank, in which precipitation of metallic ions is carried out by the subsequent addition of the following chemicals:
- Caustic soda (NaOH) to increase pH value to 8.5 – 9.5
- Flocculent, to complete flocculation
After treatment, the effluent is filtered in the filter press to remove solid waste. The filtered effluent is sent to the neutralisation tank, where the pH is corrected within the range 6.5 – 9.0 by adding sulphuric acid, before drain.
PolyWash wastewater
This effluent is collected separately from all the rest and then transferred into a reaction tank, where the pH value is lowered to 2-2.5 by adding sulphuric acid.
Potassium permanganate is then added in a quantity of 4-5%; the reaction takes about 4 hours.
Afterwards caustic soda is added to reach a pH value of 9.5-10, before dosing a quantity of 0.5% w/v of flocculent.
Once accomplished the chemical process the basket filter enables the separation of the flocculated matter from the effluent, which is finally transferred to the neutralisation tank.